CEO Tells Staff God Appointed Him Leader During Company Meeting

The meeting was meant to be routine. More than 200 employees logged on to a scheduled company-wide Zoom call, calendars marked for project timelines and quarterly targets. For most employees, it promised the usual corporate updates. Spreadsheets. Deadlines. Strategy. Instead, what followed reportedly left many employees uncomfortable and confused. According to a former employee who later described the incident online, the chief executive opened the meeting not with business priorities but with a personal declaration. He told staff that he believed God had placed him in charge of the company. The remark reportedly changed the tone of the meeting. A Meeting That Veered off Script The company was not religion-based or affiliated with any faith. There was no indication that religion played any role in its business operations. When the CEO said his leadership came from God and addressed this before discussing day-to-day operations, it reportedly created confusion among staff. Several employees later said they were confused by the remarks. The discussion about faith continued before the meeting moved to business matters. But the shift to business didn’t take place soon enough.The meeting shifted away from planned business discussions to personal remarks. Some employees said the remarks created uncertainty about leadership decisions. Questions About Merit and Legacy After the announcement was made, many employees began to have additional questions about the reasoning behind the selected CEO. Many employees were concerned with the fact that the new CEO was not just any candidate that had been selected; he was also the son of the previous CEO. Because of this, employees reportedly questioned whether leadership was based on merit or family ties. Some employees said the incident affected morale and made them reconsider their future at the company. One former employee said morale declined after the meeting. Instead of being inspired by the statements made in the announcement, many employees began to feel like there would be limited accountability for their actions. Fallout Inside the Company Following the incident, several employees reportedly left the company, citing cultural and leadership concerns. The issue was not necessarily about the religion itself; there were many employees who shared their own beliefs. The concern stemmed from introducing personal religious beliefs into leadership messaging within a secular workplace. Employees said the blurred professional boundaries affected their trust in leadership. A Wider Debate About Power Online, reactions were swift. Some compared the episode to the old notion of the divine right of kings, where leaders claimed authority from God rather than the people they governed. Others described it as nepotism dressed in spiritual language. Commenters also raised a practical concern. When a leader presents their position as ordained, criticism can feel futile. As some commenters noted, questioning a leader who frames their authority as destiny can feel difficult. The debate continued online after the meeting. For the 200 employees who logged in expecting project updates, it was a reminder that workplace culture can shift in a moment. Not with a policy change or a merger, but with a single sentence that alters how power is perceived. And once trust is unsettled, it is rarely easy to win back.
Why Interest Rates Matter to the Stock Market?

Interest Rates Have a Major Impact on Stock Market Behaviour. The cost of borrowing money for companies & consumers will impact investors’ valuation of the stock market. If the interest rate rises, the cost of borrowing increases for both consumers & companies. The increase of borrowing costs can decrease the growth of companies, reduce profitability & make stocks less attractive. If interest rates are falling or remain constant, it allows more opportunity for companies to invest and increases investors’ confidence in being shareholders of companies. The Federal Reserve’s Role The Federal Reserve is responsible for managing short-term interest rates in America. Changes to interest rates made by the Fed influence many aspects of the entire economy, including loan rates, mortgage rates, and corporate financing. Furthermore, the Fed’s action to increase or reduce interest rates has an effect on long-term bond yields. Investors utilise long-term bond yields as a way to evaluate their expected future company earnings in 10 years in today’s terms. Even though interest rates are at levels greater than during the last ten years, the stock markets have continued to show strength, coupled with interest rates decreasing and corporations continuing to show good earnings growth. How Rates Affect Stock Valuations Generally, stable or lower interest rates support the prices of stock, as they allow companies to refinance debt and expand operations or to see how things will play out in the future. At the same time, investors tend to pay higher prices for stocks when interest rates are lower because they believe the company will earn a greater amount of money in the future. Therefore, the lower or more stable an investor can get in terms of interest rates, the more likely he/she is to purchase that stock at a higher price. What Bond Yields Signal to Investors Yields on long-term bonds show us a lot about both inflation and economic growth. When yields fall due to lower expected levels of inflation while still showing stable levels of economic growth, there is often a positive response in the equity market. In contrast, when yields increase due to concerns over inflation or government bond debt, investors normally take a more cautious approach with their investment strategy, typically demanding stronger levels of corporate earnings. Interest Rates and Market Sectors Stock market sectors and industries will have a different response to changes in interest rates. Certain sectors will benefit from a drop in interest rates, while others require a strong demand for goods/services or a certain level of growth driver to benefit from falling rates. The recent trend among investors has been to pay closer attention to companies’ performances and earnings than to interest rates themselves. Looking Ahead Increasing interest rates will continue to have an impact on the stock market, but there are also a number of other factors that influence the stock market – such as corporate earnings, economic growth and long-term planning. Therefore, long-term investors that concentrate on long-term goals typically achieve better results than those that constantly adjust their investments based upon interest rate changes.
Guide to Hyper-Personalisation: Benefits, Use and Real Examples
Today’s customers demand that brands really know them as individuals; generic offerings and one-size-fits-all messages are no longer effective. Customers are seeking content, products, and/or services that reflect their preferences, habits, and timing. Hyper-personalisation is the next progression in this evolution. It takes the basis of traditional personalisation and deepens it to be able to create hyper-personalised experiences for each individual person on an ongoing basis and in real time. What Is Hyper-Personalisation? When we refer to hyper-personalisation, we mean using customer data to create experiences that are perceived as being unique to each individual user on each occasion in which they interact with a brand. Hyper-personalisation allows you to create individualised experiences instead of categorising users into broad categories or groups. Hyper-personalisation also examines items such as the user’s browsing history and previous purchases, where they are currently located, what their current actions are, and all other relevant items in order to create an experience that is relevant to the particular user at that time and place. Hyper-personalisation aims to create a sense of usefulness from every single experience instead of creating a feeling of randomness from each experience with the user. Why Hyper-Personalisation Matters When customers find content that is relevant to them, they feel as though you understand their needs. As a result, customer satisfaction increases and long-lasting relationships are created with customers. Additionally, businesses benefit because relevant offers lead to increased sales and improved conversion rates. Over time, delivering personalised experiences to customers will lead to repeat purchases, decreased customer attrition, and increased total customer lifetime value. How Businesses Can Implement It At the heart of hyper-personalisation is the need for complete and cohesive customer data; the information needs to come from different sources, such as the web, mobile devices, purchase activity, and customer service interactions, all aggregated into one view. Businesses must then put into place systems that make real-time decisions regarding what the customer is to be shown. Experiences should be evaluated and refined over time to maintain relevance and delivery effectiveness. Real-World Use Across Industries Hyper-personalisation is used by online retailers to present customers with products they are most inclined to purchase. Banks use hyper-personalisation to provide customers with useful financial insights based on their habits when they spend their money. Healthcare platforms deliver reminders and health advice specific to each patient. Travel providers use hyper-personalisation to recommend trips and to offer upgrades based on previous travel experience. Customer support will use hyper-personalisation to address a customer’s issues with the most relevant information, allowing them to resolve issues quicker and with greater detail. Final Thoughts Hyper-personalisation helps businesses stand out by making customers feel valued. When done responsibly and thoughtfully, it improves experiences, builds loyalty, and drives growth.
Data Monetisation: Stop Losing Money on Information You Already Have
What Is Data Monetisation? Most organisations gather large quantities of data on a daily basis, but they only utilise that data within their own internal reports. At the same time, companies competing against those organisations will utilise virtually the same dataset to create revenue-generating products and/or services through a method called data monetisation. To monetise data means to leverage existing datasets to extract value from it; and as such, the initial cost of acquiring the data is now generating income instead of just being an expense. Why Data Is a Business Asset Businesses need to regard information as working capital (as opposed to something that simply takes up space). For example: The transactional history of an enterprise, how users behave, telemetry received from their machines, and their customers’ character all possess true economic value in the marketplace. When they are cleaned up, organised, and packaged properly, these types of data could help to resolve issues encountered by other organisations. Therefore, businesses that create systems designed specifically to explore, convert, and present data will reap the rewards of having continued income streams versus only occasional viewpoints. Hidden Revenue in Everyday Operations Many businesses don’t realise they’re collecting valuable data even before they collect it. User clicks demonstrate the way users interact online; payment and refund data provide evidence of fraud and product problems early in the purchasing process; supply chain data reveal changes in the demand for products or markets; profiles of customers help illustrate why customers choose to buy; and, finally, device and sensor data provide evidence of how products are performing in the real world. As a result, this type of information can be costly for others to recreate; consequently, it is considered to be an asset. Turning Raw Data Into Revenue It doesn’t get very far with a good idea about making money off data and executing it properly. Companies need to determine what data is more valuable than the cost of storing it. Systems need to be created that allow for future growth and return reliable data-driven answers to assist in better decision-making. Raw data must be converted to readable answers so that users do not have difficulty in understanding them. The most effective data product integrates smoothly into the user’s workflow, and so the user will use the product reliably. What Successful Data Monetisation Looks Like Data monetisation can cut expense items, increase income items, and help with better decision-making when executed properly. Predictive analytics can help avoid equipment breakdowns. Retail analytics data helps to enhance both sales and inventory forecasting. Payment analytics data reduces fraud and chargebacks. The one common theme across these items is the focus on genuine problems that exist in business rather than on sexy types of technology.
Saks Global Shuts Most Off-Price Stores to Refocus on Luxury Retail
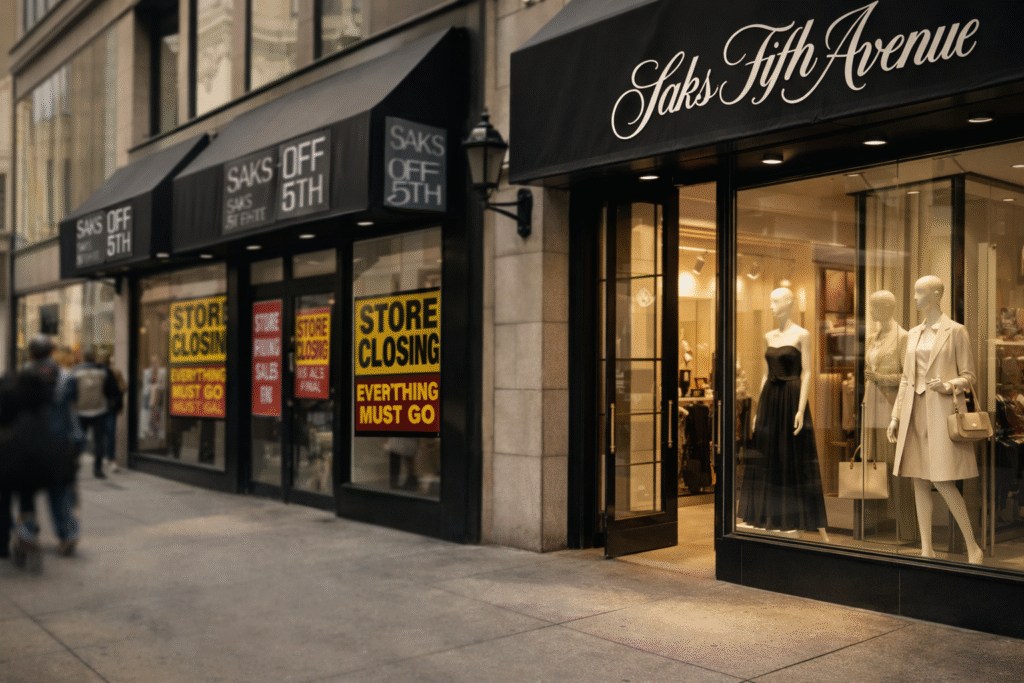

According to Saks Global, they have made the decision to close the majority of their off-price locations. As a result, the majority of the Saks Off 5th stores and all of the Last Call stores will be permanently closed. Out of 69 Saks Off 5th stores, 12 will remain open and 57 will be closing. All five of the Last Call stores will also be closing. This comes after the closure of nine of the Saks Off 5th stores last November. E-Commerce Business to Shut Down Saks Off 5th’s online business is shutting down. The eCommerce division was separated from the brick & mortar stores five years ago and is now being liquidated. An online liquidation sale started recently. Saks Global recently filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, and this has greatly accelerated the decision-making process for these particular stores. Focus Shifts Back to Luxury According to Saks Global, the move is a step toward fully committing to the luxury retail segment, further solidifying their belief in the viability of the luxury retail segment despite other retail challenges throughout the industry. “As we focus on luxury retailers, we believe we can grow with our business and our high-end customers while also promoting more full-price sales of our core brands: Saks Fifth Avenue, Neiman Marcus, and Bergdorf Goodman.” He added, “With this emphasis, we are looking to sustain our growth for many years into the future.” Why Off-Price Is Hard to Manage According to retail specialists, it is challenging to have both a full-price and an off-price business. With proper management, off-price outlets do not negatively impact full-price sales, but with off-price outlets growing and traditional department stores shrinking, off-price retailers need to establish separate strategies and excellent execution to help them sell off excess inventory. New Role for Remaining Stores The other Saks Off Fifth locations will play an increasingly smaller role going forward. Rather than purchase brand new items specifically for an off-price environment, they will sell excess inventory from Saks Global’s portfolio of luxury brands. Most of the locations that remain open now are concentrated in Florida, with dispersed locations in New York, California, Georgia, New Jersey, and Texas. One of the New York stores is experiencing leasing issues due to lack of rent payments. What This Means for Competitors Nordstrom may gain customers by expanding its off-price Rack stores, which can help with this retreat. Retail armchair experts believe that there is a tremendous amount of opportunity for luxury off-price; however, the only way to take advantage of that opportunity is for companies to commit to having a complete off-price division.
Breakthrough Medical Research That You May See in the Next Decade

There has never been a time when medical science has advanced faster than today. Revolutionary new treatments, improved diagnostic tools, and significant technological advances are just some of the exciting changes that will transform the way we approach prevention, diagnosis, and treatment over the next 10 years. Below are several of the exciting breakthroughs to expect in the future. 1. Gene Editing and CRISPR Advances The use of gene editing technology such as CRISPR-Cas9 has generated considerable media attention due to the promise it holds to change the way we treat DNA and thereby change the course of genetic disease. In the coming 10 years, scientists will continue to advance these technologies and develop methods to help eliminate diseases such as cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia, and perhaps some types of cancer, through greater accuracy and lessening the undesirable side effects of current treatment options. If successful, gene editing may soon offer patients with previously unmanageable illnesses a standard means for treating their conditions. 2. Personalized Medicine Data from patient care, which includes genetics, environments, and lifestyles, is used in personalized or precision medicine to customize the treatment a patient receives. The continued advancement of genomic science and the application of data analytics to these fields will allow for increased accessibility to personalized therapies within the next several years. The above example illustrates that the potential exists for the development of targeted therapies for a variety of conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases (e.g., heart disease), and diabetes, which could allow for more specific and efficacious therapy selection without the usual trials and errors associated with traditional prescribing methods. 3. Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics AI is changing how physicians identify and diagnose illness via machine learning algorithms through analyzing medical images, laboratory tests, and patient information quicker and often with greater precision than individuals. In the next ten years, AI may play an important role in improving the early identification of Alzheimer’s disease, lung cancer, and heart disease. With this increased accuracy in diagnosis, there is a high probability that millions of lives will be saved through early intervention. 4. Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cells Repairing or replacing damaged tissues & organs is the objective behind regenerative medicine. Stem cell-based therapy, bioengineered organs, and 3D-printed tissue all represent cutting-edge developments within this field of study. With the likely availability of heart regeneration, spinal cord injury repair, and rent tissue production scheduled for the next ten years, a new horizon appears to be approaching for many people who have experienced illness due to lack of proper care or have no access to a suitable replacement organ. 5. Advances in Immunotherapy The application of immunotherapy in the treatment of cancer has revolutionized the way in which cancer is treated and has created new ways to treat additional conditions such as autoimmune diseases, infections, and neurological disorders. In the next decade, as researchers continue to find more precise and targeted immunotherapy options, the treatments that they develop will likely be less toxic and more effective than current methods. 6. Longevity and Anti-Aging Research Science is increasingly focused on extending healthy lifespan. Research into senescence, cellular repair, and metabolic pathways may soon lead to therapies that slow aging and reduce age-related diseases. The next decade could bring medications or treatments that help people live longer, healthier lives while maintaining quality of life. 7. Telemedicine and Digital Health Innovations The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, wearable devices, and remote monitoring tools. In the next ten years, these technologies will become more integrated and sophisticated, allowing doctors to monitor patient health in real time, predict illnesses, and provide care from anywhere. This shift will improve access to healthcare, particularly in remote or underserved regions. 8. Microbiome-Based Therapies Researchers are discovering that the human microbiome—the collection of microbes living in our bodies—plays a critical role in health. Future treatments may involve modifying gut bacteria to prevent or treat conditions like obesity, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, and even mental health issues. Microbiome-based therapies could revolutionize how we understand and maintain health. Conclusion The next decade promises a remarkable transformation in medicine. From gene editing and AI-powered diagnostics to regenerative therapies and anti-aging research, these breakthroughs could redefine healthcare as we know it. While challenges remain, including regulatory hurdles and ethical considerations, the future of medicine looks brighter than ever, offering hope to millions around the world.
Rupee Falls to 92 Against US Dollar: What It Means for Your Daily Expenses and the Indian Economy

The value of India’s currency has reached its lowest value ever recorded (92 rupees for every dollar), and as of January 23rd has seen some strengthening back to 91.88 rupees. This continued decline has begun to impact families, businesses, and students as the prices of many everyday items have increased. This ongoing depreciation of the rupee is attributed to many factors, including foreign investors selling their holdings in Indian markets; weak domestic stock market performance due to global economic concerns; and the resulting capital flight towards the stronger US dollar. The rupee depreciation has been approximately 2% thus far in January and nearly 5% over the last year, demonstrating that there is continuing downward pressure on the currency. Imports Become More Expensive The weakening of the Indian Rupee means that it will cost Indians more rupees to buy the same amount of crude oil that is priced in US dollars, which raises the cost of importing crude oil and is a concern for India as 85% of India’s crude oil consumption comes from imports. When crude oil prices rise, so do gasoline, diesel, and transportation costs, and as a result, prices of food and other daily items increase. In addition to crude oil, India also imports electronics, coal, chemicals, machinery, fertilizer, gold, and edible oils. Thus, the rising price of crude oil will lead to increasing prices for products such as mobile phones, home appliances, cars, and electronic devices. Foreign Education and Travel Hit Hard International students will not only be burdened by rising costs I.E Tuition, Living & Accommodation but with everything paid on an annual basis they now have to exchange more funds from Indian Rupee to purchase USD, which ultimately will lead to higher overall expenditures. Furthermore, flights and travel have also increased as more conversions of INR -> USD are needed to pay for airfare, lodging, and other travelling costs. A Small Relief for Some Not everyone loses from a weaker rupee. Non-resident Indians (NRIs) benefit because money sent home converts into more rupees. This boosts remittances and supports many families. Exporters See Mixed Impact Exporters generally gain when the rupee weakens, as their goods become cheaper and more competitive globally. They also earn more rupees for every dollar received. However, sectors that rely heavily on imported raw materials — such as electronics, gems, and jewellery — may see profits reduced due to higher costs. Industries with lower import dependence, like textiles, may benefit more. The Road Ahead India’s imports recently rose to $63.55 billion, widening the trade deficit. Experts suggest that policymakers must carefully balance growth and inflation, while improving trade and currency strategies to protect the economy from further shocks. For now, the falling rupee means one thing for most Indians: higher costs at home and abroad.
How to Create a Unique Selling Proposition (USP) That Makes Your Business Stand Out

Customers are surrounded by endless choices. Every company claims to offer the best quality, the lowest prices, and excellent service. Because of this, it becomes difficult for buyers to decide which brand they should trust. If your business sounds the same as everyone else, customers may simply move on without noticing you. This is where a Unique Selling Proposition, commonly known as a USP, becomes essential. A clear and strong USP helps your business stand out, communicate value quickly, and give customers a strong reason to choose you over competitors. Understanding the Meaning of a USP The USP provides clarity on your business because this is a short, easy-to-read and understand phrase that defines how your business is different from other businesses and shows why your product or service is superior to the competition. This statement emphasises the unique benefits of your product or service and is based on everything that you can provide that no one else can. Rather than listing general “guarantee” promises, a USP focuses on specific benefits that are important to your customers. The USP will answer 3 primary questions: What do I have to offer? Who can benefit from my products and services? And how are my products and services the best option for my customers? When you know the answers to these questions, you will have a strong and memorable brand message. Why Every Business Needs a USP Lacking a unique selling proposition (USP), many companies will have trouble getting attention. Many companies invest time and resources in advertising but don’t convert visitors into customers because their message is unclear. A clearly articulated USP establishes customer confidence, as it gives customers exactly what they can expect from the business as it relates to their needs. A clearly defined USP improves marketing campaigns, strengthens branding, and generates higher sales by targeting a more relevant market. When customers see how they fit into the company’s value proposition, they will be more likely to purchase from the business again. A strong USP is essential to the growth of a business. Knowing Your Target Audience The first step in creating an effective USP is understanding your target audience. You must know who your customers are and what problems they face in their daily lives. When you understand their needs, challenges, and preferences, you can position your product as the perfect solution. For example, busy professionals may look for convenience and speed, while families may prefer affordability and reliability. Your USP should speak directly to these needs. When customers feel that your brand understands them, they naturally feel more connected to your business. Studying Your Competition After identifying your audience, it is important to study your competitors carefully. Observing what others are offering helps you discover gaps in the market. Many businesses repeat the same claims about quality or service, which makes them sound identical. By analysing their strengths and weaknesses, you can find opportunities to offer something better or different. Perhaps competitors deliver slowly, charge higher prices, or provide poor customer support. These weaknesses give you the chance to position your brand uniquely and create a USP that fills those gaps effectively. Identifying Your Core Strengths Once you know your customers and competitors, focus on your own strengths. Think about what your business does exceptionally well. It could be faster delivery, better technology, personalised service, or years of expertise. Sometimes, the smallest detail can become your biggest advantage. Customer feedback can also reveal hidden strengths, as people often mention what they appreciate most. By identifying these qualities, you can craft a message that highlights your true value. Concentrating on one or two strong points makes your USP clear and powerful rather than confusing. Writing a Clear and Memorable Statement When writing your USP, simplicity is key. Long or complicated sentences can weaken your message and make it hard to understand. Instead, use clear and direct language that focuses on benefits rather than features. Your statement should immediately show how customers will benefit from choosing your business. A short and memorable sentence is easier to communicate across websites, advertisements, and social media platforms. The goal is to create a message that stays in the customer’s mind and makes your brand easy to recognise. Testing and Refining Your USP Creating a USP is not a one-time task. As markets change and customer preferences evolve, your message may need adjustments. Testing different versions of your USP through marketing campaigns can help you understand which one performs better. Customer feedback and sales results provide valuable insights into whether your message is effective. Refining your USP over time ensures that it continues to stay relevant and impactful. Businesses that regularly improve their messaging often see stronger engagement and better results. Conclusion A unique selling proposition is more than just a tagline; it is the heart of your brand identity. It clearly communicates why your business deserves attention and how it solves customer problems better than anyone else. By understanding your audience, studying competitors, recognising your strengths, and crafting a simple message, you can create a USP that drives growth and builds loyalty. In a crowded marketplace, being different is not just helpful but necessary. A strong USP ensures that your business is remembered, trusted, and chosen every time.
Before You Launch an AI Startup, Read This: 7 Deadly Mistakes Founders Regret
Starting an AI-based company sounds exciting. Artificial intelligence is transforming industries like healthcare, finance, marketing, and e-commerce. Many founders jump into AI startups thinking technology alone will guarantee success. But reality is different. Building an AI company needs the right mix of business thinking, data strategy, ethics, and customer focus. Many promising AI startups fail not because the idea is bad, but because of avoidable mistakes made early on. If you are planning to build an AI-driven company, avoiding these common mistakes can save you time, money, and frustration. Mistake 1: Building Technology Without a Real Problem One of the biggest mistakes founders make is starting with technology instead of a real problem. Many AI startups focus on what their model can do rather than what customers actually need. AI should solve a clear pain point, not exist just because it sounds impressive. Before writing a single line of code, talk to potential users, understand their challenges, and confirm they are willing to pay for a solution. A problem-first approach gives your AI product real value and market demand. Mistake 2: Ignoring Data Quality and Availability AI systems are only as good as the data they learn from. Many startups assume data will be easy to collect or clean later. This is a costly assumption. Poor quality, biased, or incomplete data leads to inaccurate results and unreliable AI models. Before launching, founders must ensure they have access to sufficient, relevant, and legally usable data. Investing early in data collection, cleaning, and governance builds a strong foundation for long-term success. Mistake 3: Overestimating AI Capabilities Another common mistake is overpromising what AI can deliver. Some founders believe AI can replace human intelligence completely or work perfectly from day one. In reality, AI systems need training, testing, and continuous improvement. Unrealistic promises can damage trust with customers and investors. It is better to be transparent about limitations and show steady improvement over time. A realistic roadmap builds credibility and long-term relationships. Mistake 4: Not Having the Right Team An AI company needs more than just developers. Many startups fail because they hire only technical talent and ignore business, legal, and domain experts. A strong AI team includes data scientists, engineers, product managers, industry specialists, and ethical advisors. Business strategy, user experience, and compliance are just as important as algorithms. A balanced team ensures your AI solution is usable, scalable, and market-ready. Mistake 5: Ignoring Ethics, Privacy, and Compliance AI companies handle sensitive data, which makes ethics and compliance critical. Many startups delay thinking about data privacy, bias, and regulations until problems arise. This can lead to legal trouble, customer backlash, and reputational damage. Regulations like GDPR and data protection laws must be considered from the start. Building ethical AI practices early creates trust and protects your company as it grows. Mistake 6: Focusing Only on the Product, Not the Customer Some AI founders become so focused on improving models and accuracy that they forget about the user experience. Customers care about outcomes, not algorithms. If your AI tool is difficult to use or does not integrate with existing systems, adoption will suffer. Regular feedback, user testing, and simple design help ensure your AI product fits smoothly into real-world workflows. Mistake 7: Scaling Too Fast Without Validation Rapid scaling is tempting, especially when investors show interest. However, scaling an AI company without validating product-market fit is risky. Expanding too early can drain resources and amplify unresolved issues. Start small, test your solution in controlled environments, learn from feedback, and refine your model. Sustainable growth comes from proven value, not rushed expansion. Conclusion Setting up an AI-based company is both challenging and rewarding. Success depends not only on advanced technology but also on smart decisions made early in the journey. By avoiding these seven common mistakes, founders can build AI companies that are ethical, customer-focused, and scalable. A thoughtful approach helps turn AI innovation into real business impact.
How AI Is Changing Sales Strategies and Performance

The use of artificial intelligence by sales teams is growing rapidly. This is because AI provides sales professionals with a greater ability to understand customer needs and predict future purchase behaviour, allowing them to target and focus their efforts on the most profitable customers. Artificial intelligence can improve sales performance, create more effective sales strategies and, ultimately, improve a salesperson’s ability to perform successfully. What Is Artificial Intelligence in Sales? Artificial intelligence employs methods that enable machines to learn autonomously from experience. This use of AI as an intelligent assistant provides sales organisations with the ability to interact with potential customers more efficiently by keeping track of all previous communications and purchases made by those prospects. AI capabilities include predictive analytics, conversational interfaces, and content generation, all of which enable organisations to streamline daily sales activities. Why Sales Teams Need AI Today The competitive nature of sales has increased, and consumers are now very knowledgeable. Today, the majority of consumers utilise online/Internet resources to learn about products prior to speaking with a salesperson. Thanks to AI, teams of sales representatives can leverage technology to perform their jobs efficiently; this includes faster access to information, the ability to automate routine activities, and equipment for focusing on selling (closing) deals. By providing sales teams with up-to-date data, AI is reducing the time it takes to do an excellent job while also increasing their accuracy when it comes to forecasting, planning, etc. Improving Productivity and Forecasting AI eliminates many repetitive tasks, such as generating reports and data entry. By freeing up time for salespeople to concentrate on building strong customer relationships and converting leads into customers, AI enables sales teams to be more productive than ever before. The use of AI to analyse large amounts of data helps to generate superior sales predictions, enabling businesses to prepare for inevitable changes, such as market fluctuations, changes in consumer behaviour, or seasonal variations, thereby avoiding unpleasant surprises. Personalising Customer Experiences With AI, sales teams can analyse past customer interaction history to determine what their customers want. This enables salespeople to provide tailored communications with suggested products and contact customers at optimal times for each individual. Understanding customers generates positive feelings, builds trust and usually leads to increased sales. Smarter Sales Actions and Coaching AI is capable of evaluating sales calls and emails to determine effective and ineffective practices and provide data for managers to use for coaching and enhancing team productivity. Based on information obtained through the AI tool, the suggestions made by the AI will dictate the next best course of action that should occur to close a deal, such as when to contact a lead next, the information to send, etc. Challenges of Using AI in Sales Companies face many potential challenges when applying artificial intelligence in their business models. Some organisations have difficulty integrating artificial intelligence tools into their current operating environment. If data used for training purposes does not meet an acceptable level of quality, the level of effectiveness achieved by artificial intelligence will be impaired. There may also be privacy-based concerns with the artificial intelligence application, as well as employee reluctance due to uncertainty regarding the use of new technology. Appropriate employee training and effective communication regarding potential uses of artificial intelligence will alleviate these concerns. The Future of AI in Sales As we move towards 2026, Artificial Intelligence (AI) will become increasingly important for sales professionals. AI will not replace sales representatives but rather aid them within their existing roles. When used properly, AI provides sales teams with better tools for improving their customer relationships, providing a higher level of service, and producing improved sales results.
