Why Iran Attacked US Data Centres in the Gulf

In a dramatic escalation of regional tensions, Iranian strikes targeted data centres operated by Amazon Web Services in the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain. The attacks mark a significant shift in modern conflict: technology infrastructure is no longer collateral damage. It is now a primary objective. The strikes came days after a joint US-Israeli operation reportedly eliminated senior Iranian leadership, including Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei. With conventional military targets already hit, Iran’s response appears aimed at economic, technological and strategic pressure points. What Happened to AWS Facilities? According to company statements, Iranian drone strikes hit an AWS cloud unit in the UAE, while a blast near another facility in Bahrain caused structural damage and power disruptions. Although Amazon described the damage as limited, parts of the affected infrastructure were temporarily shut down. Customers were advised to back up data as recovery efforts continued. The market reaction was swift. Amazon shares fell roughly 2.7 per cent in premarket trading following reports of the strikes, underscoring investor sensitivity to geopolitical risk in critical infrastructure. Data Centres as Strategic Targets The attacks reflect a broader reality: data is central to modern power. If oil refineries were prime targets in 20th-century wars, data centres are their 21st-century equivalent. These facilities require billions in capital investment and support everything from banking transactions to government communications. The Gulf region, particularly the UAE and Bahrain, has positioned itself as a rising hub for artificial intelligence and cloud computing infrastructure. Major technology companies have poured resources into the region, encouraged by political stability and large-scale investment commitments. Disrupting these assets sends a powerful signal — both economically and symbolically. Striking high-value digital infrastructure can undermine investor confidence and challenge the perception of regional security without necessarily escalating to full-scale ground conflict. AI and Military Operations Another possible motive relates to artificial intelligence in warfare. Reports indicate that US military planners relied on advanced AI tools, including systems developed by Anthropic such as Claude, for intelligence analysis, target identification and battlefield simulations during recent operations. Modern militaries depend heavily on cloud computing to process vast amounts of data. Intelligence gathering, satellite imagery analysis, communications and operational modelling all rely on secure data infrastructure. By targeting AWS facilities in the Gulf, Iran may have sought to disrupt or complicate regional information flows that support US and allied military activities. Even temporary outages can slow logistics, data processing and coordination. In this context, attacking data centres could be viewed as an attempt to counter the technological advantages demonstrated in earlier strikes. Economic Ripple Effects The third potential motive lies in the interconnected nature of cloud services. A single data centre does not serve one client. It supports thousands of businesses simultaneously. From financial institutions to logistics firms, many rely on cloud infrastructure for daily operations. Damaging such facilities can create cascading effects. Even limited outages can disrupt transactions, communications and data access across multiple sectors. In a globalised digital economy, hitting one facility can ripple outward across borders. The immediate dip in Amazon’s stock price highlights how sensitive markets are to disruptions in core digital infrastructure. The Gulf’s Stability Questioned The Gulf region has recently been marketed as the next global AI and technology hub. High-profile visits and multi-trillion-dollar investment pledges reinforced that narrative. However, the strikes raise questions about the resilience of that positioning. If data centres can become frontline targets, the perceived safety of hosting critical infrastructure in geopolitically sensitive areas may be reassessed. While AWS has emphasised redundancy and recovery protocols, the symbolic impact of the attacks could prove as significant as the physical damage. A New Phase of Warfare The targeting of data centres illustrates how warfare is evolving. Beyond military bases and energy facilities, digital infrastructure now sits firmly within the strategic calculus. Three motives appear plausible: economic disruption, interference with AI-supported military operations, and the ability to affect multiple organisations with a single strike. As conflicts increasingly intertwine with technology, the battlefield extends beyond land, sea and air — into server rooms and cloud networks. The Gulf strikes suggest that in modern war, data itself has become a target.
Humongous Numbers of People Are Uninstalling ChatGPT as Anti-OpenAI Sentiment Surges

A sharp backlash is unfolding against OpenAI after CEO Sam Altman announced a new agreement with the US Department of Defence. Fresh app intelligence data suggests the outrage is translating into action, with large numbers of users uninstalling ChatGPT and turning to rival platforms. According to figures reported by TechCrunch and attributed to market intelligence firm Sensor Tower, uninstalls of the ChatGPT mobile app surged by 295 per cent on Saturday compared with the previous day. That spike far exceeds the chatbot’s typical day-over-day uninstall rate of roughly nine per cent over the past month. The data marks one of the most dramatic short-term reversals in user sentiment since ChatGPT’s launch. Fallout From the Pentagon Deal The controversy began after OpenAI confirmed a deal to provide artificial intelligence tools to the US Department of Defence. Critics argue that the agreement could allow advanced AI systems to be used in military planning or operations, intensifying ethical concerns that have followed the industry’s rapid growth. In online forums and social media threads, some users accused OpenAI of compromising its earlier public positioning around AI safety. One widely shared post on Reddit called on subscribers to cancel paid plans and share proof of their cancellations. Others posted guides explaining how to export ChatGPT conversation histories and migrate to competing services. Altman attempted to address the backlash during a live question-and-answer session on X, but critics continued pressing the company over the scope of its military involvement. Claude Gains as Users Jump Ship. Much of the departing traffic appears to be heading toward Anthropic and its chatbot, Claude. Anthropic has publicly stated that it would not allow its AI systems to be used in autonomous weapons or for mass domestic surveillance. While questions remain about how AI tools may ultimately be deployed in defence contexts, the company’s stance appears to have resonated with users. Sensor Tower data cited by TechCrunch shows that Claude installs rose 37 per cent day-over-day on Friday and an additional 51 per cent on Saturday. Over the weekend, Claude climbed to the top position in the US App Store, overtaking ChatGPT, which slipped into second place. For the first time, US downloads of Claude reportedly surpassed those of ChatGPT. Growth Slows for ChatGPT The controversy has not only affected uninstalls. It has also dampened new user growth. Download growth for ChatGPT dropped 14 per cent day-over-day on Saturday, followed by a further five per cent decline the next day. Just one day before the backlash intensified, growth had been running at a positive 13 per cent. Such swings highlight how quickly public perception can shift in the highly competitive AI market. While ChatGPT remains one of the most widely used AI applications globally, its dominant position is no longer unchallenged. A Test for the Broader AI Industry The episode underscores a deeper tension shaping the artificial intelligence race: the balance between commercial expansion, government partnerships, and public trust. AI companies increasingly rely on enterprise and government contracts to fund large-scale model development. At the same time, consumer adoption depends heavily on perceptions of safety, transparency, and ethical use. Whether the backlash proves temporary or signals a longer-term shift remains uncertain. App rankings can fluctuate rapidly, and uninstall spikes do not always translate into permanent losses. However, the scale of the reaction suggests that defence partnerships carry reputational risks in an industry built on public goodwill. For now, the numbers tell a clear story. A 295 per cent surge in uninstalls is more than routine churn. It reflects a moment of reckoning for OpenAI — and a reminder that in the AI era, public opinion can move just as quickly as the technology itself.
Bitcoin Price Jumps 8%; Breakout Hopes Reignite Across Crypto Markets

Bitcoin has staged a strong comeback, climbing 8% and reclaiming the psychologically crucial $70,000 level. The move has reignited bullish sentiment across crypto markets, with traders closely watching whether the rally can extend toward new short-term highs. After consolidating above key support zones earlier this week, BTC gathered momentum and broke through multiple resistance levels in quick succession. A rally above $70,000 signals strength. Bitcoin formed a solid base above the $67,500 region before pushing past the $68,800 resistance zone. The breakout accelerated as bulls drove the price decisively above $70,000, triggering renewed buying interest. The rally peaked near $74,062, where selling pressure emerged. A modest pullback followed, with BTC slipping below $73,000 and retracing toward the 23.6% Fibonacci level of the upward move from the $66,164 swing low to the $74,062 high. Despite the correction, Bitcoin continues to trade comfortably above $70,000 and remains above its 100-hourly simple moving average — a key short-term bullish indicator. Adding to the positive structure, a bullish trend line is forming on the hourly chart with support near $68,000, reinforcing the broader uptrend. Key Resistance Levels to Watch If Bitcoin stabilises above the $70,000 threshold, the next immediate resistance sits near $72,800. This level is critical in determining whether bulls can regain full control. The first major resistance lies around $73,500. A sustained close above this zone could open the door for another test of $74,000. Should momentum accelerate, upside targets extend to $75,000. Beyond that, technical projections suggest potential barriers near $76,800 and $77,200. A clean break above these levels would significantly strengthen the bullish narrative and raise expectations of a broader breakout phase. However, traders remain cautious, as price action near prior highs often attracts profit-taking. Is a Downside Correction Possible? Failure to clear the $72,800 resistance could trigger another pullback. Immediate support lies near $72,200, followed by the stronger $72,000 zone. The next major support sits around $70,000, which also aligns with the 50% Fibonacci retracement of the recent upward move. Holding this level is crucial for maintaining bullish momentum. If selling pressure intensifies, BTC could revisit $68,800 support in the near term. The primary structural support remains at $68,000. A break below this trend line support would weaken the short-term outlook and potentially delay further upside attempts. Technical Indicators Overview Major Support Levels: Major Resistance Levels: Market Sentiment Turns Optimistic The 8% surge has revived breakout expectations across crypto markets, especially as Bitcoin defends higher support levels. While consolidation remains possible in the near term, the broader technical structure suggests that bulls still have room to push higher — provided key resistance levels are cleared. For now, the $70,000 level stands as the line in the sand. As long as Bitcoin holds above it, the path of least resistance may remain to the upside.
Over $700 Million in 24 Hours: How Much Could the Iran War Cost America?

As US and Israeli strikes on Iran intensify under Operation Epic Fury, the financial cost of the conflict is mounting at a rapid pace. While the human toll continues to rise across the region, policymakers and analysts are now grappling with another critical question: how much will this war ultimately cost the United States? Early figures suggest that even in its opening hours, the campaign has come with a staggering price tag. The First 24 Hours: A $700 Million Start According to estimates cited by Turkey’s Anadolu news agency, the United States may have spent approximately $779 million in the first 24 hours of Operation Epic Fury alone. This figure includes air operations, missile launches, logistics, and the deployment of high-end military hardware across the Middle East. Prior to the first strike, the Pentagon had already invested heavily in repositioning aircraft, deploying naval vessels, and reinforcing regional bases. Al Jazeera reported that this pre-strike military build-up cost an additional $630 million. The rapid mobilisation reflects the scale of the operation. Fighter aircraft deployed under US Central Command included F-18s, F-16s, F-22s, and F-35s. Based on projected flight hours, maintenance requirements, and munition usage outlined in recent Department of Defence budget documents, early air sorties are estimated to have cost roughly $271 million. Beyond fighter jets, the US has deployed specialised aircraft such as the EA-18G Growler for electronic warfare, A-10C Thunderbolt attack aircraft, MQ-9 Reaper drones, and other unmanned systems. Each platform carries its own operating and maintenance costs, adding to the growing total. The Daily Cost of Naval Power Even without ground troops deployed at scale, maintaining a significant naval presence in the region is expensive. The Center for New American Security estimates that operating a carrier strike group, such as the USS Gerald R. Ford, costs approximately $6.5 million per day. If multiple carrier groups remain in the region for several weeks, operational costs could quickly reach hundreds of millions of dollars. These figures cover fuel, personnel, maintenance, and aircraft operations aboard the carrier and its escort ships. Missile defence interceptors, drone surveillance missions, and intelligence-gathering operations further increase daily expenditures. If President Donald Trump’s suggested timeline of four to five weeks holds, the cumulative operational costs could multiply rapidly. Lessons From Past Conflicts History suggests that initial combat expenses often represent only a fraction of a war’s eventual price tag. The war in Afghanistan, which lasted nearly 20 years, cost trillions. According to reporting by the Associated Press, Congress allocated just over $1 trillion to the Department of Defence specifically for Afghan operations. However, when broader costs were included — such as Pentagon base budget increases, State Department reconstruction funding, interest on borrowed funds, and long-term veterans’ care — the total exceeded $2.3 trillion. Veterans’ medical and disability costs alone reached approximately $465 billion through fiscal year 2022. Harvard scholar Linda Bilmes has projected that future care obligations for Iraq and Afghanistan veterans could add another $2 trillion by 2050. More recently, Brown University’s Costs of War project estimated that since the October 7, 2023 Hamas attack on Israel, the US has spent $21.7 billion in military aid to Israel. Additional regional military operations have cost between $9.65 billion and $12.07 billion. Combined, those expenditures exceed $31 billion — and counting. These examples illustrate how quickly war-related spending can expand beyond initial battlefield operations. Energy Markets and Indirect Economic Impact Beyond direct Pentagon spending, there are broader economic risks. The conflict has already unsettled oil markets. Any threat to the Strait of Hormuz — a key maritime route through which a significant share of global oil passes — could send crude prices higher. Rising energy costs would likely fuel inflation in the United States and impact global economic growth. Such indirect consequences do not appear in military budgets but can impose substantial costs on households and businesses through higher fuel prices and supply chain disruptions. An Uncertain Timeline President Donald Trump has described Operation Epic Fury as decisive but open-ended. Speaking at the White House, he said the campaign was initially projected to last “four to five weeks” but added that the US has the capability to continue for longer if necessary. Defence Secretary Pete Hegseth has insisted the conflict will not become “endless”, while acknowledging that further American casualties are possible. On the ground, the violence continues. Iranian authorities report hundreds of fatalities across multiple cities, while Israel and Lebanon have also recorded casualties. Missile exchanges and air operations remain ongoing, underscoring the volatility of the situation. The Bottom Line In just one day, Operation Epic Fury has reportedly cost the United States more than $700 million. With naval forces deployed, advanced aircraft flying daily missions, and regional tensions rising, the financial burden is likely to grow with each passing week. Whether the conflict concludes within the projected timeline or stretches further will determine whether this becomes a short, high-intensity campaign or another prolonged and expensive chapter in America’s military history.
What US Bases Did Iran Target And Were Any Americans Killed
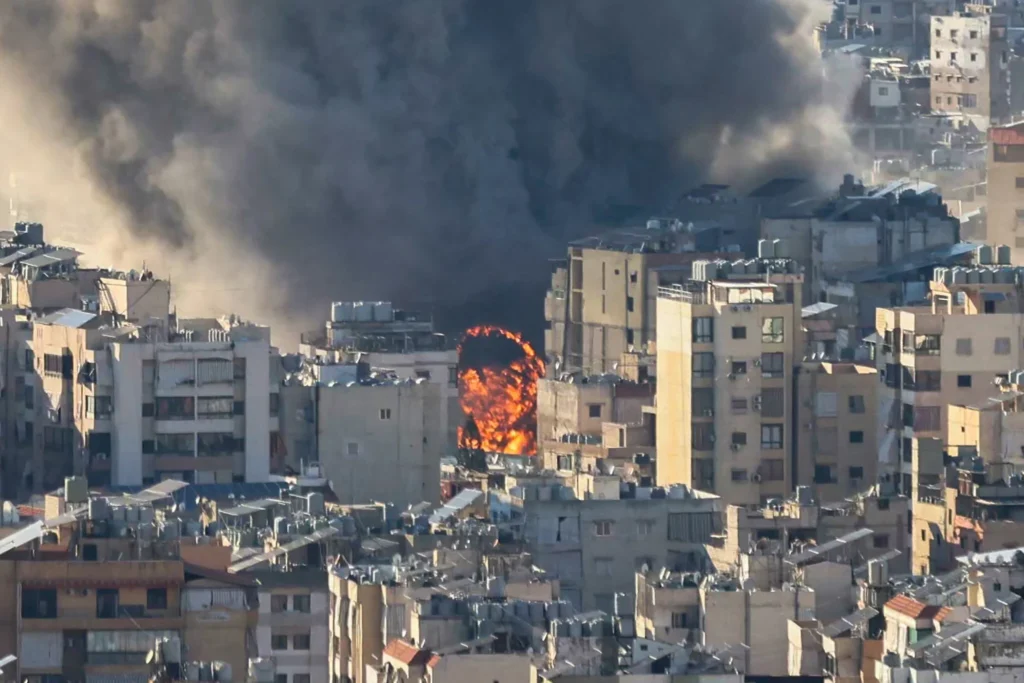

Iran launched a sweeping wave of missile and drone attacks across the Middle East on 28 February, striking locations where US forces are stationed. The barrage came hours after US Israeli strikes on Iranian targets. The immediate question in Washington was stark. Were any American servicemembers killed? According to the US military, the answer is no. No American Casualties Reported United States Central Command said it successfully defended against hundreds of incoming missiles and drones. In a statement, it confirmed there were no US casualties and no combat related injuries. Officials added that damage to installations was minimal and did not disrupt operations. Between 30,000 and 40,000 US troops are deployed across the region on any given day. The scale of the assault therefore raised serious concern about the potential human toll. Bahrain Fifth Fleet Targeted One of the most visible strikes hit near the headquarters of the United States Navy Fifth Fleet in Bahrain. Video verified by multiple outlets showed a missile landing close to the naval facility, sending smoke into the air. Bahraini authorities confirmed an attack on the area. The base plays a central role in US maritime operations in the Gulf. Al Udeid And Gulf Bases Under Fire Missiles were also fired at Al Udeid Air Base in Qatar, the forward headquarters of Central Command. Qatari officials said air defences intercepted the incoming projectiles. In Kuwait, Ali Al Salem Air Base came under attack. Three members of Kuwait’s armed forces sustained minor injuries from falling debris, though no US personnel were reported harmed. Explosions were heard near Al Dhafra Air Base in the United Arab Emirates. Erbil in Iraq, home to a US air facility, was also struck. Jordan reported intercepting missiles targeting areas near Muwaffaq al Salti Air Base. A Region On Edge The attacks extended across Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Jordan, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates. Social media footage showed missiles streaking across night skies and air defence systems activating over urban centres. The Pentagon described the strikes as retaliation for US Israeli operations that targeted Iranian military infrastructure, including Revolutionary Guard command sites and missile launch facilities. Heavy Casualties Reported In Iran While US forces reported no fatalities, Iranian state media said more than 200 people were killed and over 700 injured in strikes inside Iran. Among the dead were dozens reportedly at a girls’ school in the south of the country. The contrast is stark. US bases endured a coordinated assault but avoided loss of American life. Inside Iran, the human cost appears far higher. For now, the region remains on alert. Military installations are fortified. Air defences are active. Diplomacy is strained. The question is no longer only who was targeted. It is whether this exchange marks a contained episode or the opening chapter of a wider confrontation.
The Role of Influencer Marketing in American Businesses

Marketing in the United States has changed dramatically over the past decade. Traditional advertising methods like television, radio, and print are no longer the only ways to reach customers. Today, brands connect with audiences through social media platforms, and one strategy stands out above the rest — influencer marketing. Influencer marketing has become a powerful tool for American businesses of all sizes. From startups to global corporations, companies are partnering with social media creators to build trust, increase visibility, and drive sales. But why has this strategy become so effective in the US market? Let’s explore its growing role and impact. What Is Influencer Marketing? Influencer marketing is a strategy where businesses collaborate with individuals who have a strong online following. These influencers promote products or services to their audience through platforms like Instagram, TikTok, YouTube, and Facebook. Unlike traditional advertisements, influencer promotions feel more personal and authentic. Followers trust influencers because they see them as relatable individuals rather than corporate brands. This trust plays a major role in influencing purchasing decisions. In the US, consumers value recommendations from real people. When an influencer shares their experience with a product, it often feels like advice from a friend rather than a sales pitch. Why Influencer Marketing Works in the United States The US has one of the largest social media user bases in the world. Millions of Americans spend hours daily scrolling through content, watching videos, and engaging with creators. This makes social media platforms ideal for brand exposure. Another reason influencer marketing works well in the US is the strong culture of personal branding. Many influencers build communities around specific interests such as fitness, beauty, finance, gaming, parenting, or technology. Businesses can partner with influencers whose audience aligns perfectly with their target market. For example, athletic brands like Nike frequently collaborate with fitness influencers to promote new product launches. Similarly, beauty brands often work with creators who specialize in makeup tutorials and skincare advice. The result is targeted marketing that reaches the right audience without wasting advertising dollars. Types of Influencers American Businesses Use Not all influencers have millions of followers. In fact, many US companies prefer working with micro-influencers — creators with smaller but highly engaged audiences. These influencers often have stronger personal connections with their followers. There are generally four categories: Mega influencers, often celebrities or public figures with millions of followers. Macro influencers, with large audiences and strong brand presence. Micro influencers, with smaller but loyal communities. Nano influencers, everyday users with highly niche audiences. American businesses often combine different types depending on their goals. Large corporations may focus on broad awareness campaigns, while small businesses may prioritize local micro-influencers to drive targeted traffic. Benefits of Influencer Marketing for American Businesses One major benefit is increased brand trust. Consumers are more likely to buy from a brand recommended by someone they follow regularly. This emotional connection improves conversion rates. Another advantage is cost efficiency. Compared to traditional advertising, influencer partnerships can offer better returns, especially for small and mid-sized businesses. Influencer marketing also improves social proof. When followers see others using a product, it creates a sense of popularity and reliability. Brands like Glossier built massive growth in the US by focusing heavily on influencer-driven strategies rather than traditional advertising. This demonstrates how powerful authentic online promotion can be. Challenges Businesses Face Despite its benefits, influencer marketing comes with challenges. Choosing the wrong influencer can damage a brand’s image. If an influencer’s audience does not match the company’s target market, the campaign may fail. There are also risks related to authenticity. If promotions feel forced or overly scripted, audiences may lose trust. Another challenge is measuring return on investment. While likes and shares are easy to track, direct sales attribution can sometimes be more complex. American businesses must carefully analyze influencer engagement rates, audience demographics, and campaign goals before investing. Influencer Marketing and Small Businesses in the US Influencer marketing is not only for big brands. Small businesses across the United States use local influencers to grow visibility and build community trust. For example, a local restaurant might partner with a food blogger in their city. A boutique clothing store may collaborate with a fashion creator who has a loyal regional audience. These partnerships often cost less than large advertising campaigns but deliver strong local impact. Because consumers increasingly value authenticity, smaller creators can sometimes drive better results than celebrity endorsements. The Future of Influencer Marketing in America The influencer marketing industry in the US continues to evolve. Short-form video content is growing rapidly, especially on platforms like TikTok and Instagram Reels. Live streaming, affiliate marketing, and performance-based influencer partnerships are also becoming more common. Data-driven strategies are shaping the future. Businesses are now using analytics tools to evaluate engagement rates, conversion metrics, and audience insights before launching campaigns. As consumers become more selective about advertising, influencer marketing will likely focus more on transparency and long-term partnerships rather than one-time promotions. What Makes an Influencer Campaign Successful? Successful campaigns usually have clear goals. Whether the objective is brand awareness, website traffic, or direct sales, businesses must define measurable outcomes. Authenticity is also key. Influencers should genuinely align with the brand’s values. Audiences can quickly recognize when promotions feel unnatural. Finally, strong communication between the business and influencer ensures that messaging stays consistent while allowing creative freedom. When done correctly, influencer marketing builds long-term brand loyalty rather than short-term exposure. Final Thoughts The role of influencer marketing in American businesses is stronger than ever. It bridges the gap between brands and consumers by creating personal, relatable connections. In a competitive and digitally driven market like the United States, businesses must adapt to changing consumer behavior. Whether you are a startup or an established brand, influencer marketing can increase trust, visibility, and engagement when used strategically. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, one thing remains clear — people trust people more than ads. And that is why influencer marketing will continue to shape the future of
Franchise vs. Independent Business: What Works Better in the US?

Starting a business in the United States is a big decision. One of the first questions entrepreneurs face is whether to buy a franchise or start an independent business from scratch. Both options offer exciting opportunities, but they come with very different paths, risks, and rewards. Understanding how each model works can help you choose the right direction for your goals, budget, and personality. Let’s explore what works better in the US market and why. Understanding the Franchise Model A franchise is a business model where you purchase the rights to operate under an established brand name. Well-known examples include companies like McDonald’s, Subway, and 7-Eleven. When you buy a franchise, you pay an initial fee and ongoing royalties in exchange for brand recognition, training, and operational support. The biggest advantage of a franchise in the US is brand trust. Customers already recognize the name, which makes it easier to attract business from day one. Franchisors also provide systems, marketing support, and detailed operating procedures. This reduces the guesswork that comes with starting a business. However, franchises come with strict rules. You must follow the company’s guidelines for branding, pricing, suppliers, and operations. There is limited creative freedom. The initial investment can also be high, especially for popular national brands. Franchising works well for entrepreneurs who prefer a proven system over experimentation and want lower risk compared to starting from scratch. Understanding the Independent Business Model An independent business is built entirely from your own idea. You create the brand, design the services or products, and make all operational decisions. This could be anything from a local coffee shop to a tech startup or consulting firm. The main advantage of an independent business is full control. You decide everything — branding, pricing, marketing strategies, suppliers, and growth direction. There are no royalty fees, and profits belong entirely to you. In the US, independent businesses can thrive because of the country’s strong entrepreneurial culture and access to funding options. Small Business Administration (SBA) loans and local grants often support independent startups. However, independent businesses carry higher risk. There is no established brand reputation. You must build trust from the ground up. Marketing costs may be higher initially, and mistakes can be expensive without corporate guidance. This path suits entrepreneurs who are creative, innovative, and comfortable with uncertainty. Cost Comparison: Which Is More Affordable? In the US market, franchise startup costs vary widely. Some franchises require investments of $50,000, while others may exceed $500,000. On top of the initial fee, you often pay ongoing royalties and marketing contributions. Independent businesses may start with lower upfront costs depending on the industry. A home-based service business, for example, can be launched with minimal investment. However, without brand recognition, you may spend more on marketing and customer acquisition. If you have limited capital, an independent business may offer more flexibility. If you have access to financing and prefer structured support, franchising may justify the higher cost. Risk and Success Rates in the US Many people believe franchises are safer than independent businesses. While franchises do benefit from established systems, success still depends on location, management, and market demand. In the US, franchise businesses often show stable performance because of proven business models. However, they are not risk-free. Poor management or oversaturation in a local market can lead to failure. Independent businesses have higher variability. Some fail quickly, while others grow into major brands. Think about companies like Apple or Amazon, which started as independent ventures before becoming global giants. The key difference is that independent businesses carry higher risk but also unlimited growth potential. Flexibility and Innovation If innovation excites you, independent businesses offer more freedom. You can pivot your strategy, test new products, or rebrand anytime. In fast-changing industries like technology or digital marketing, this flexibility can be a huge advantage. Franchise owners must follow corporate rules. Major decisions are controlled by the franchisor. While this ensures consistency, it can limit local creativity. In the competitive US market, adaptability is often a major success factor. Independent businesses can respond quickly to trends, while franchises move more slowly due to centralized decision-making. Brand Power vs. Personal Vision Franchises offer instant brand power. Customers already trust familiar names. This is especially important in industries like food service, fitness, and retail. Independent businesses rely on personal vision. You build something unique that reflects your values and creativity. For many entrepreneurs, this sense of ownership is deeply rewarding. The question becomes: Do you want to manage a proven system, or build something entirely your own? What Works Better in the US? There is no single answer. The US market supports both models strongly. Franchises perform well in standardized industries where customers value consistency. Independent businesses thrive in innovative sectors where uniqueness matters. If you prefer structure, lower uncertainty, and brand recognition, franchising may be the better option. If you value independence, creativity, and long-term scalability, starting your own business might be more rewarding. Your decision should depend on your financial capacity, risk tolerance, industry interest, and long-term goals. Final Thoughts Choosing between a franchise and an independent business is one of the most important decisions an entrepreneur will make. Both models can succeed in the United States, but they require different mindsets. A franchise offers security and support. An independent business offers freedom and unlimited potential. Take time to research your industry, evaluate your strengths, and consider your comfort with risk. The right choice is not about which model is better overall — it is about which one is better for you.
Bill and Hillary Clinton to Testify Before House Panel in Epstein Probe
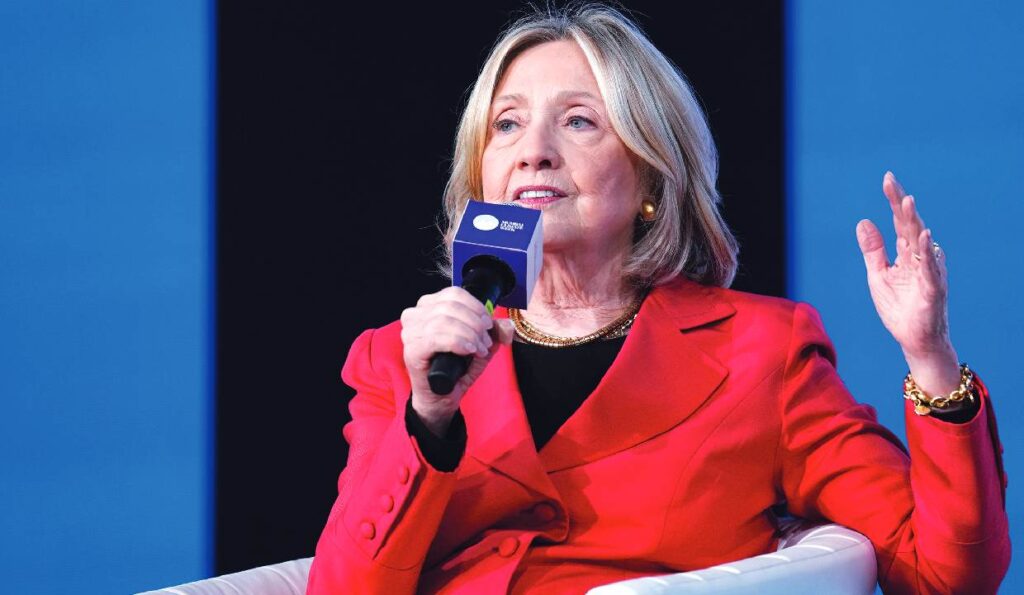

House Committees investigating former sex offender Jeffrey Epstein and his associate Ghislaine Maxwell are scheduled to take deposition testimony from both former President Bill Clinton and former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton. The depositions of the Clintons will take place in Chappaqua, New York, where they reside. The testimony of Hillary Clinton is expected to take place on Thursday, while the deposition of Bill Clinton is expected to take place on Friday. Both deposition sessions will be recorded and transcribed. According to James Comer, Chair of the House Committee on Oversight and Reform, the committee wants transparency and accountability for victims and the general public. Last month, the Clintons agreed to give testimony via teleconference at a House committee hearing after they had previously telephoned the House Republican leadership and stated their intention to work with the committee to provide testimony by providing documents; however, previously they were unwilling to appear in person in what they considered to be a political witch hunt. Links in Released Documents Documents from the U.S. Department of Justice that name Bill Clinton as having travelled with Jeffrey Epstein are contained in his flight logs for 2002 and 2003. The logs include travel to Thailand, Portugal, Ghana, Russia and China. The trips occurred before Epstein was convicted of prostitution involving underage girls in 2008. The files also contained photos and a birthday card with Bill Clinton’s name, handwritten by Ghislaine Maxwell. Over 700 times Hillary Clinton’s name is listed in the documents that were made public; predominantly, these are articles located from 2016 covering her presidential run – and all handed out to Epstein. In addition, there have been questions regarding whether or not Maxwell attended the Clinton Global Initiative meeting in 2013. At the BBC Clinton has stated that Maxwell’s association from this meeting is not what the essence of the entire courtroom scenario should be; furthermore, she also stated that the primary concern of this case should remain focused upon the crimes committed against the female/male children who were victimised.
Ethical Use of AI in Modern Businesses
AI is beginning to take root in businesses. The use of AI (chatbots answering customer enquiries & software/software development predicting sales trends) makes it possible for companies to operate rapidly & intelligently. As such, there is much demand for the ethical use of AI. Companies should recognise that unethical uses have the potential to harm rather than help humans. Why Ethics Matters in AI Data is the basis for decision-making in AI. If the data being used is biased or has gaps, then there is the potential for unfair outcomes. For example, when a hiring tool has been trained with only limited amounts of information, it may not be obvious when an AI system is giving favourable results to one group compared to another. Ethical use of AI requires ensuring that data is checked for fairness, systems are tested regularly to ensure fair outcomes and that decisions are transparent. Companies should always be able to answer, “Does this technology benefit all individuals equally?” Protecting Privacy and Data Today’s companies gather massive stores of customer data, and this information can allow AI systems to analyse past customer transactions in order to improve future customer experience and other areas. In addition to the large databases of collected customer data that modern companies operate, every customer also trusts the companies they engage with to hold their private data securely and keep this data safe via data protection laws and the development of appropriate security systems. Ethical use of AI technology will require organisations to treat customer information with respect and protect customers’ confidential information by being clear about how they collect customer data and what they are going to use customer data for. Human Oversight and Accountability AI must augment human decision-making rather than completely displacing human judgement. There are times when a machine needs to make a decision for which there must be human oversight (e.g., approving loans, screening applicants). In the event an AI makes a mistake, it is the responsibility of the company, not the technology, to accept responsibility. When a company shows it will take responsibility when there is a mistake made by the technology, it will help establish trust amongst customers and employees. Building Trust Through Responsible AI When using AI ethically, an organisation establishes trust with its customers and employees, building long-term confidence to allow companies to develop strong reputations. Using AI ethically involves creating value responsibly, not only avoiding difficulties. The modern world more than just defines success by profit; it also defines success in terms of responsibility and technology usage.
Student Loan Forgiveness and Its Economic Impact

Student loan forgiveness has become one of the most debated economic policies in the United States. For millions of Americans struggling with education debt, it represents financial relief and a fresh start. But for economists and policymakers, it raises tough questions about inflation, fairness, and long-term fiscal impact. With repeated proposals and partial rollouts under the administration of Joe Biden, the issue has moved from campaign promise to economic reality. The big question now is simple: does student loan forgiveness help the economy, or does it create new risks? A Lifeline for Millions of Borrowers Student debt in the US has crossed $1.7 trillion, affecting over 40 million borrowers. Many graduates carry loans for decades, delaying major life milestones like buying a home, starting a business, or saving for retirement. Loan forgiveness programs aim to ease this burden by reducing or eliminating part of the debt. For individuals, the benefits are immediate. Lower monthly payments increase disposable income, giving borrowers more room to spend, invest, or save. For younger Americans especially, this can feel like a reset button on their financial future. Boost to Consumer Spending One of the biggest short-term economic benefits of student loan forgiveness is increased consumer spending. When borrowers are freed from large monthly payments, they tend to spend more on everyday goods, travel, housing, and services. This surge in spending can stimulate local economies, especially in urban areas where student debt levels are higher. Some economists compare the effect to a targeted stimulus package. Instead of sending checks to everyone, forgiveness directs money toward people who are likely to spend it quickly. This can boost GDP in the short run and support businesses recovering from economic slowdowns. Impact on Homeownership and Entrepreneurship Student debt has long been blamed for delaying homeownership among younger Americans. With less debt, borrowers may find it easier to qualify for mortgages, potentially boosting the housing market. Similarly, loan forgiveness may encourage entrepreneurship. Many potential business owners avoid taking risks because of heavy loan obligations. Reducing debt could lead to more startups, innovation, and small business growth. In theory, this could create jobs and strengthen economic dynamism over time. Inflation Concerns While the benefits sound promising, critics warn that student loan forgiveness could fuel inflation. If millions of borrowers suddenly have more money to spend, demand for goods and services may rise. In an already inflation-sensitive economy, this could push prices higher. The Federal Reserve closely monitors such policy changes because consumer spending directly affects inflation trends. Some analysts argue that large-scale forgiveness could complicate the Fed’s efforts to control rising prices. However, others believe the inflation impact may be limited, especially if forgiveness is gradual or targeted. The Taxpayer Debate Another major controversy is who ultimately pays for loan forgiveness. Student debt does not simply disappear—it is absorbed by the federal government, meaning taxpayers indirectly bear the cost. Critics argue this creates fairness issues, especially for people who never attended college or already repaid their loans. Supporters counter that education benefits society as a whole, and relieving debt can create broader economic advantages. They also point out that the government has historically supported industries and financial systems during crises. The debate often comes down to ideology: personal responsibility versus collective benefit. Effects on the Federal Budget From a fiscal perspective, large-scale loan forgiveness increases government spending. This adds pressure to an already high national debt. Some experts worry that repeated forgiveness programs could signal fiscal looseness, potentially affecting investor confidence and long-term borrowing costs. However, others argue that the real economic impact depends on how forgiveness is structured. Targeted programs for low-income borrowers may cost less while delivering stronger economic benefits. In short, the budget impact is significant but not straightforward. Moral Hazard and Future Borrowing Another concern is the message loan forgiveness sends to future students. If borrowers expect loans to be forgiven later, they may be less cautious about borrowing. Colleges might also feel less pressure to control tuition costs, potentially driving education prices even higher. This phenomenon, known as moral hazard, is a key reason why many economists advocate for reforms alongside forgiveness—such as tuition caps or changes to the student loan system. Without structural changes, forgiveness alone may not solve the root problem. A Divided Economic Verdict Economists remain divided on the long-term impact of student loan forgiveness. Supporters see it as a social investment that reduces inequality, boosts consumption, and helps younger generations build wealth. Critics view it as a costly policy that shifts burdens onto taxpayers while doing little to fix systemic issues in higher education. The truth likely lies somewhere in between. The economic effects depend heavily on scale, timing, and targeting. What Comes Next? Student loan forgiveness is unlikely to disappear from the policy debate anytime soon. Future administrations may expand, modify, or reverse existing programs depending on political priorities and economic conditions. What is clear is that student debt has become a defining financial issue for an entire generation. Whether through forgiveness, reform, or a mix of both, the US will need long-term solutions. The real challenge is balancing compassion for borrowers with economic stability—a task that will shape fiscal policy for years to come.
